Ciudad Politécnica de la Innovación
Innovation news
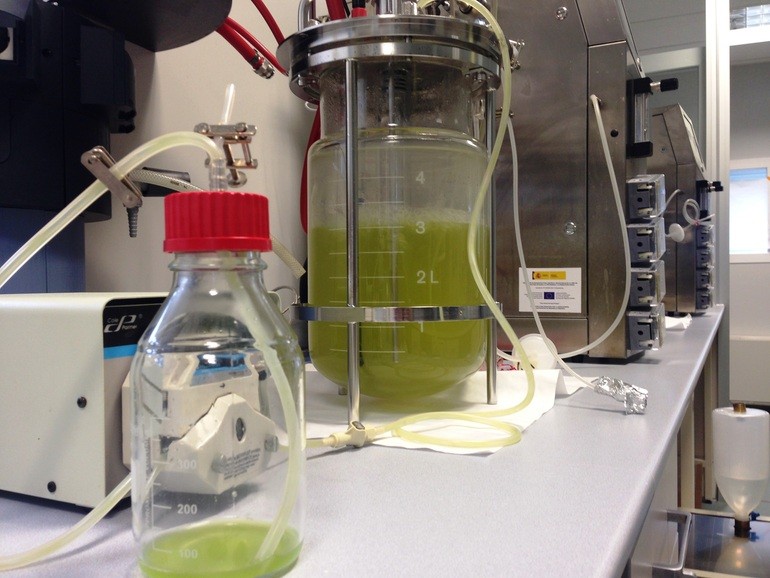
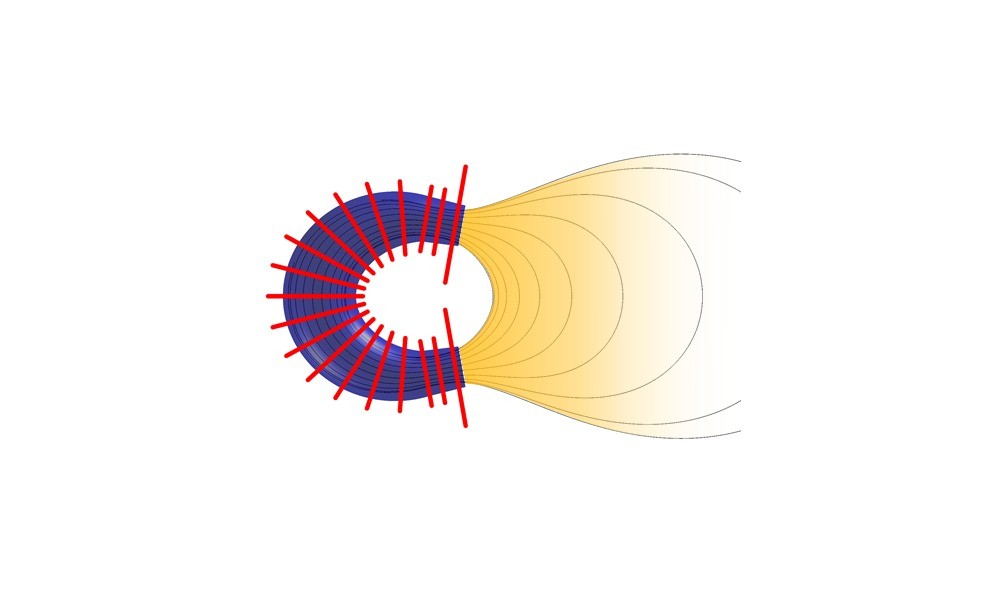
A new plasma engine will allow less expensive, more efficient, and longer space missions
Parque Científico de la UC3M
The Malaga-based company Ingenia releases an Open Source application for the fight against COVID-19
Parque Tecnológico de Andalucia
SinFin Energy: technology transfer from the mile of knowledge
Gijón Science and Technology Park
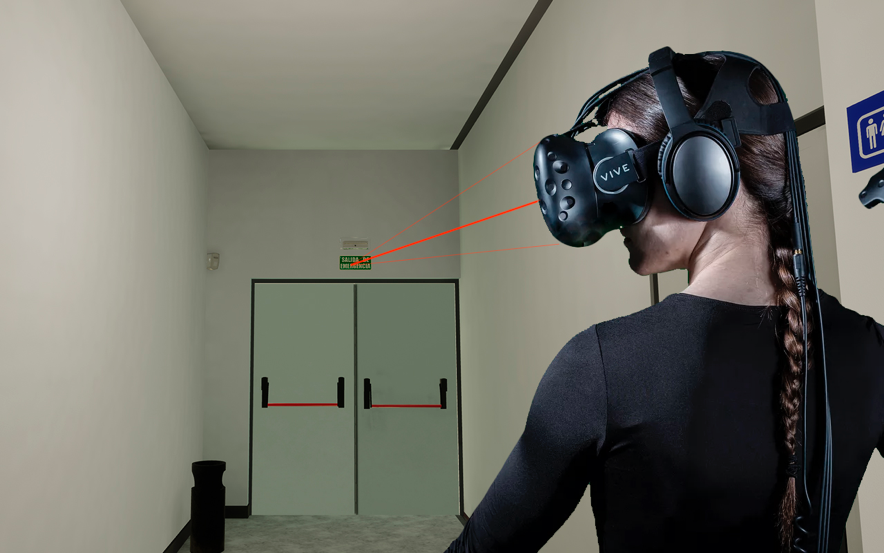
6DLab, from UC3M Science Park applies virtual reality for the Mapfre Foundation
Carlos III University of Madrid Science Park – Leganés Tecnológico
PITCHING ROBOTS WITH THE LOOK, IT IS A REALITY
ABB and Irisbond today introduced the first practical demonstration of their joint development to control robots using eye-tracking technology, the result of collaboration under the BIND 4.0 program ABB and Irisbond today presented…
RECYCLING OF MEMBRANES USED IN DESALATION ALLOWS THE REUSE OF RESIDUAL WATER
The importance of water is vital; Is a finite and vulnerable resource that must be taken care of to achieve the objectives of sustainable development. Only 3% of the planet's…
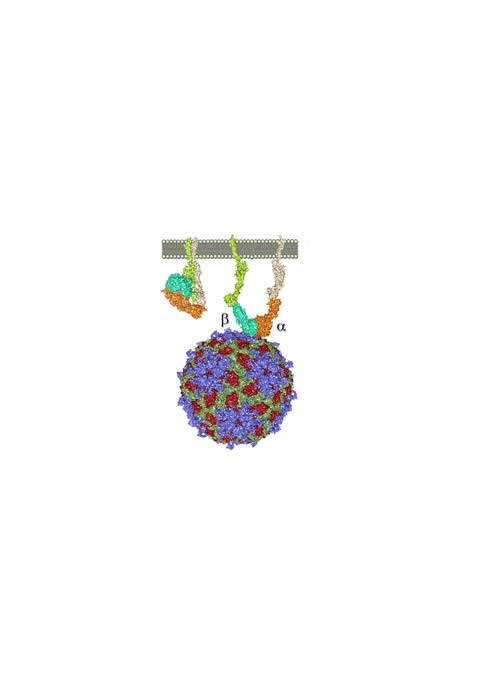
CIC BIOGUNE RESEARCHERS REVEAL THE STRUCTURAL COMPLEXITY OF THE ARCHAEAN DNA REPLICATION MACHINERY AND THE INTERACTION OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS WITH ITS CELL RECEPTOR
Both papers, co-led by researcher Ikerbasque Nicola GA Abrescia, have been published in the journal Nature Communications The study on the interaction of foot-and-mouth disease virus with its cellular receptor, integrin alfaVbeta6, will allow the design of inhibitors of virus entry In both investigations a key role has been played by electron microscopy, fundamental for the compression of cellular mechanisms, including the entry of viruses into cells Researchers at CIC bioGUNE and the University of Indiana have unveiled the architecture of the archaeal DNA replication machinery assembly, a group of unicellular microorganisms capable of living in extreme conditions, and possibly the oldest forms of life on the earth. "More than 30 years after their first characterization, we have discovered that PolyB1 DNA polymerase from Sulfolobus is a heterotrimeric holoenzyme. Therefore, assemblages with multi-subunits of the DNA polymerase are found in the three domains of life: eucaria, bacteria and archaea. Our work demonstrates how the association with accessory subunits can affect the central activity of a replicative DNA polymerase, improving its efficiency during genome duplication, a fundamental cellular process in all domains of life, "says Nicola GA Abrescia, Professor Ikerbasque In CIC bioGUNE. The relevance of this finding, which has been published in the journal Nature Communications, lies in the understanding of the cellular DNA replication mechanism, using archaea as a simplified model system of much more complex eukaryotic processes. It should be noted that this research may have biotechnological applications, and different companies in this sector are interested in the use of highly stable enzymes, such as…